Sun protection according to skin type: How to choose the best protection for your skin
Bright sunlight, endless beach days and balmy summer evenings – the warm weather has arrived at last and invites us to enjoy the sun to the fullest. Here, you’ll find out what influence the melanin content of your skin has on sun protection and how to find out your skin type so you can choose the best protection for you.
24 May 2023 • 4 min. reading time
Table of contents
What does the right sunscreen for your skin type mean and how long can you spend in the sun without burning?
Generally, the paler your skin, the higher the SPF should be in your sun cream. Because there is a direct connection between the melanin content of your skin and your natural skin tone.
The skin pigment melanin protects your skin from sunburn. The higher the melanin content, the higher the sun protection. Whereas people with darker skin types can spend longer than average in the sun without their skin burning, lower levels of melanin are present in people with paler skin tones.
Find out your skin type for the best sun protection
You can tailor your individual requirements for sun protection by doing a skin type test. Since 1975 the scale of the US dermatologist Thomas B. Fitzpatrick has been used, which is divided into six skin types. It is, however, worth noting that the boundaries are fluid when it comes to determining skin type. So if in doubt, you should seek the advice of a professional dermatologist.
The classification of the six skin types is based on laboratory measurements and respondent surveys. The following table gives you an overview of the division of the skin types:

However, this division should not be used for children. Children’s skin is generally particularly light-sensitive and very thin. The skin’s ability to produce pigmentation and its own protective mechanisms are not sufficiently pronounced and developed in children. Their skin is therefore always at risk from UV radiation regardless of skin type. The skin can only protect itself fully once we have reached our teenage years.
What skin type do I have – is sun or shade the order of the day?
Certain characteristics help to find out your skin type and adapt your sun protection accordingly. Eye and hair colour are, however, often not the decisive clues. Above all, people with relatively pale skin should consider whether they tan quickly in the sun.
Skin type 1: The amount of time you can spend in the sun without burning is very short
Freckles and quickly getting sunburnt are typical signs of extremely pale skin type 1, as is red or blonde hair. With this type, the skin tans only slightly or not at all. The amount of time you can spend in the sun without burning is less than 15 minutes. In summer you require a sunscreen that provides at least SPF 50. Furthermore, it's better if you stay in the shade in summer. You are at risk of getting sunburnt, especially at noon. It is best to wear a sun hat and light clothing in the sun.
Skin type 2: Skin goes red relatively quickly
Freckles are also a classic feature of skin type 2. Whereas the skin only lightly tans, the hair is mostly blonde, light brown or dark brown. With this skin type, you can spend between 10 and 20 minutes in the sun without burning. There is good reason to use an SPF 50 sunscreen, especially without prior tanning. After a week’s holiday or with a below-average UV index, SPF 30 can sometimes be enough.
Skin type 3: This skin type rarely gets sunburnt
With the medium-pale skin type 3, you can tan relatively quickly. At the same time, brown and dark blonde hair is a feature of this type. Although sunburn is to be feared less frequently than with the two paler skin types, sun protection remains important. If you can spend up to half an hour in the sun without burning, on the whole, at least SPF 30 is still recommended without prior tanning.
Skin type 4: Despite quick tanning, sunscreen is indispensable
People with the olive skin (type 4) only rarely get sunburnt thanks to quick tanning. Brown or black hair is a typical feature. The amount of time that this skin type can spend in the sun without burning is around 30 to 40 minutes. When choosing a sunscreen, you shouldn't go less than SPF 20 in summer.
Skin type 5: Skincare after sunbathing is particularly important
With the dark skin type 5, your skin tans extremely quickly. With this type, the hair is often dark brown or black. Because the amount of time that can be spent in the sun without burning is around 60 minutes, sunburn is a rarity. Nevertheless, you should not underestimate UV damage from the sun. To guarantee safe protection, use sun creams with SPF 10 or 20. If you spend a very long time in the sun, you might even need SPF 30. It is also important that you nourish your skin with after-sun products after sunbathing. In doing so, you are restoring your skin’s moisture content.
Skin type 6: The risk of sunburn is minimal
The characteristics of the very dark skin type 6 are similar to those of type 5. Extensive sunbathing won't get you very far however. Your skin barely tans any further. For this reason, you are only very rarely affected by sunburn. But you should still not go without basic protection. Sun creams with SPF 10 or 15 are a good choice. However, consider using UV protection on your lips or the palms of your hands, as these areas are sensitive to the sun.
UV index – additional influence on sun protection
The UV index is a second criterion, along with your skin type, that has a decisive influence on the individual amount of time that you can spend in the sun without burning. This value is also known by the abbreviation UVI. The UV index tells you the intensity of UV radiation at different locations you can expect at the current time every day. The more intense the sun appears according to the UVI, the greater the protection your skin will need. So the UV index gives you an important reference point in selecting a sun cream with the appropriate SPF.
Above all, the following features of the location and weather influences affect the UVI:
- exact time of day
- current cloud coverage
- reflections in snow or sand
- condition of the ozone layer
- geographical height and width
As long as the UV index is at 1, there is only a low danger to health. However, the UVI scale goes up to value 11+, which is a warning of an extreme danger to health. If the UV index is above average, you should not rely on general information about sun protection according to skin type alone.
When in doubt, it is always advisable to go for a sun cream with a higher SPF and use additional sun protection measures. In addition, cloud coverage alone is no reason for ditching your sun protection because up to 50% of UV rays will often penetrate a cloudy sky. The German Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS) and the German Weather Service give daily information about the current UV index.
How long can I spend in the sun?
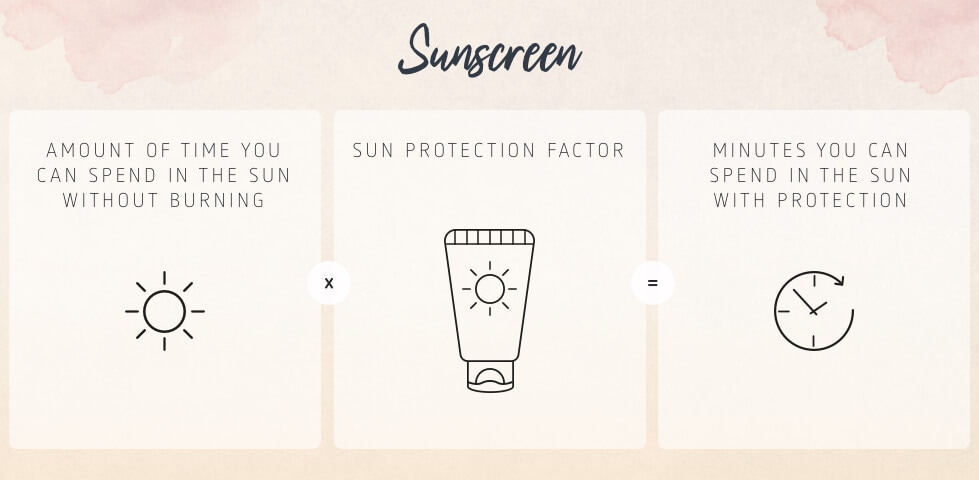
If you multiply the SPF of your sun cream with the amount of time you can spend in the sun without burning, you will get a useful indicator. The result of this calculation corresponds, as a rule, to the minutes, that you can expect to be protected in the sun. While you calculate this time you can spend in the sun without burning, you should not neglect the current UV index, along with the sun protection for your skin type, and make adjustments accordingly for the amount of time you personally can spend in the sun without burning. To avoid sunburn in the time determined, reapply your sun cream regularly.
Find the right sun protection for your skin type
Takeaway
The right sunscreen plays a decisive role in protecting your skin from the damaging effects of UV rays. Finding out your skin type helps you to choose the best sunscreen and avoid sunburn. Pale skin types need a higher SPF, while darker skin types can spend longer in the sun without burning. The UV index also plays a role in determining the time you can spend in the sun without burning. If you consider the time you spend in the sun responsibly and use a sun cream with an SPF to match your skin type, you can enjoy the warm weather without a care in the world.



































